#Health Tech
The integration of advanced technologies in European healthcare has brought about transformative changes, significantly enhancing the quality, efficiency, and accessibility of medical services across the continent. As European healthcare systems continue to face challenges such as aging populations, rising healthcare costs, and the need for personalized medicine, the adoption of cutting-edge technologies is playing a crucial role in addressing these issues. From artificial intelligence (AI) to telemedicine and electronic health records (EHRs), the impact of these technologies is profound, reshaping the way healthcare is delivered and experienced in Europe.
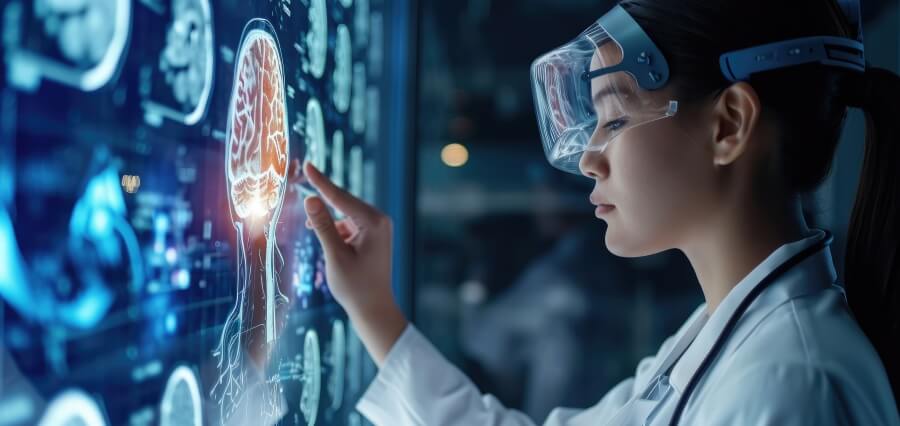
One of the most significant technological advancements in European healthcare is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. AI has revolutionized various aspects of medical care, including diagnostics, treatment planning, and patient monitoring. In diagnostics, AI-powered tools can analyze medical images, such as X-rays and MRIs, with remarkable accuracy, often surpassing human capabilities. This has led to earlier and more accurate detection of diseases, particularly in areas like oncology and cardiology, where early intervention is critical. AI algorithms also assist in predicting patient outcomes and identifying the most effective treatment plans based on vast datasets, leading to more personalized and effective care.
Moreover, AI is being utilized to optimize hospital operations and resource management. For instance, predictive analytics can forecast patient admissions, allowing hospitals to allocate resources more efficiently and reduce waiting times. This is particularly important in European healthcare systems, where managing the flow of patients and resources is a constant challenge. By improving operational efficiency, AI helps reduce costs while maintaining high standards of care, making healthcare systems more sustainable in the long term.
Telemedicine is another technology that has significantly impacted European healthcare, especially in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. Telemedicine involves the remote delivery of healthcare services through digital platforms, enabling patients to consult with healthcare providers without the need for physical visits. This has been particularly beneficial in rural and underserved areas, where access to healthcare facilities is limited. Telemedicine has also played a crucial role in reducing the burden on hospitals and clinics during the pandemic, allowing patients to receive care while minimizing the risk of virus transmission.
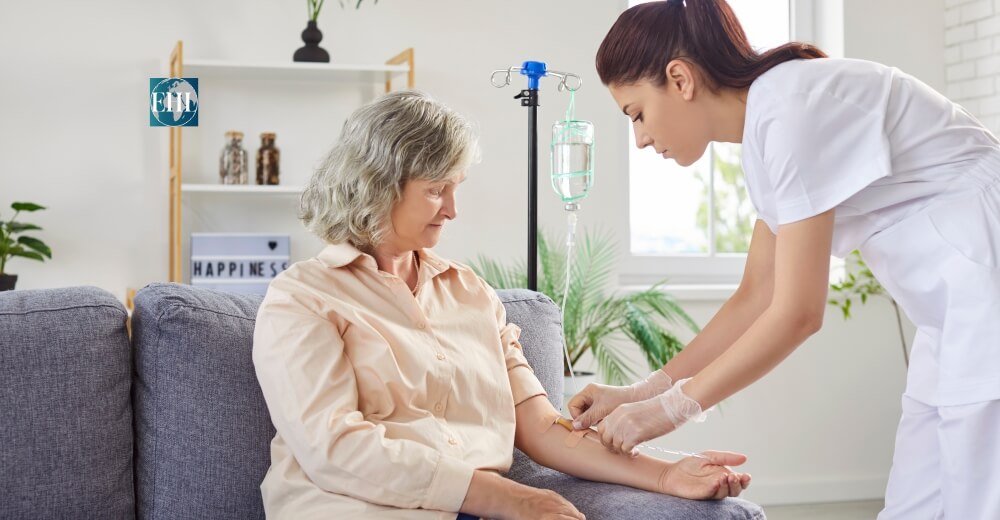
The widespread adoption of telemedicine in Europe has led to improved access to healthcare, especially for patients with chronic conditions who require regular monitoring and consultations. Patients can now manage their health more effectively from the comfort of their homes, while healthcare providers can monitor their patients’ conditions in real-time through wearable devices and mobile health apps. This continuous monitoring enables early detection of potential health issues, leading to timely interventions and better health outcomes. Furthermore, telemedicine has empowered patients by giving them greater control over their healthcare, fostering a more patient-centered approach.
Electronic health records (EHRs) have also been a game-changer in European healthcare, streamlining the management of patient information and facilitating better coordination of care. EHRs enable healthcare providers to access a patient’s complete medical history at the point of care, ensuring that all relevant information is available for making informed decisions. This not only improves the accuracy of diagnoses and treatment plans but also reduces the risk of medical errors. EHRs have also enhanced communication and collaboration among healthcare providers, leading to more coordinated and integrated care, particularly for patients with complex medical needs.
In addition to improving the quality of care, EHRs have also contributed to the efficiency of healthcare systems in Europe. By digitizing patient records, healthcare providers can reduce the time spent on administrative tasks, freeing up more time for patient care. EHRs also facilitate data sharing across different healthcare settings, such as hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies, enabling a seamless flow of information and reducing duplication of tests and procedures. This not only saves time and resources but also enhances the patient experience by reducing the need for repetitive data entry and ensuring continuity of care.
Another area where technology is making a significant impact is in the development of personalized medicine. Advances in genomics and biotechnology have enabled the tailoring of treatments to individual patients based on their genetic makeup. This approach is particularly promising in the treatment of cancer and rare diseases, where traditional one-size-fits-all treatments may be less effective. In Europe, personalized medicine is becoming increasingly integrated into healthcare systems, offering the potential for more targeted and effective treatments, as well as reducing the risk of adverse drug reactions.
Despite the many benefits of technological advancements in European healthcare, challenges remain. Data privacy and security concerns are paramount, as the increased use of digital health technologies involves the collection and storage of vast amounts of sensitive patient data. Ensuring that this data is protected from breaches and misuse is crucial for maintaining patient trust and complying with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Additionally, the digital divide poses a challenge, as not all patients have equal access to digital health tools and services, potentially exacerbating health disparities.
The modern technologies have influenced and transformed the European healthcare in a profound way, offering numerous benefits in terms of improved care quality, efficiency, and accessibility. AI, telemedicine, EHRs, and personalized medicine are just a few examples of how technology is transforming healthcare across Europe. However, to fully realize the potential of these advancements, it is essential to address the challenges associated with data privacy, security, and equitable access. As Europe continues to embrace digital health innovations, the future of healthcare looks increasingly promising, with technology playing a pivotal role in shaping a healthier and more sustainable future for all.